
|
|
EQUALITY STANDARD: One of three basic income distribution standards (the other two are contributive standard and needs standard). The equality standard distributes income equally to every person in society. Everyone--every man, woman, and child--would, in other words, receive exactly the same, per capita income--no more, no less. If, for example, total income earned by 270 million people in the United States is $7 trillion, then every person would receive $25,925.9 each--no more, no less.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           MARKET DISEQUILIBRIUM: The state of the market that exists when the opposing market forces of demand and supply do achieve a balance and there is an inherent tendency for change. Market disequilibrium results if the market is not in equilibrium. More specifically, market disequilibrium results if the demand price is not equal to the supply price and the quantity demanded is not equal to the quantity supplied. In general, disequilibrium results if opposing forces are not in balance. For market disequilibrium, the opposing forces that are out of balance are demand and supply. The result of the imbalance between these two forces is the existence of a shortage or surplus, which induces a change in the price.Shortage and SurplusMarket disequilibrium is characterized by either a surplus or a shortage. Both arise due to the inequality between quantity demanded and quantity supplied.- Shortage: A shortage exists if the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied at the current market price. This condition emerges if the market price is below the equilibrium price. With a market shortage, buyers are unable to buy as much of the good as they would like at the current price. As such, they are motivated to raise the price.
- Surplus: A surplus exists if the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded at the current market price. This condition emerges if the market price is above the equilibrium price. With a market surplus, sellers are unable to sell as much of the good as they would like at the current price. As such, they are motivated to lower the price.
Market disequilibrium exists with a surplus or shortage because the price does not remain unchanged. The imbalance between quantity demanded and quantity supplied prompts the price to change. A shortage prompts the price to rise and a surplus causes the price to fall.Out of Balance| The 8-Track Tape Market | 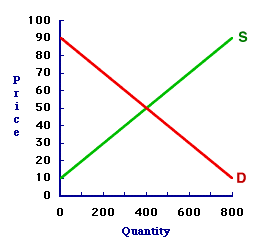 |
Market disequilibrium can be illustrated using the market for 8-track tapes displayed in this exhibit. This graph was generated after long hours attending the 88th Annual Trackmania 8-Track Tape Collectors Convention at the Shady Valley Exposition Center.- Shortage: Consider first how a shortage is created at a 30 cent price. Click the [Shortage] button to highlight this price. At 30 cents, the quantity demanded is 600 tapes and the quantity supplied is 200 tapes. This is not equilibrium. The buyers cannot buy all that they want. They want to buy 600 tapes, but only 200 tapes are offered for sale by the sellers. This shortage motivates buyers to offer a higher price. This shortage is clearly NOT equilibrium.
- Surplus: Now consider how a surplus is created at a 70 cent price. Click the [Surplus] button to highlight this price. At 70 cents, the quantity demanded is 200 tapes and the quantity supplied is 600 tapes. This is not equilibrium. The sellers cannot sell all that they want. They want to sell 600 tapes, but only 200 tapes are being purchased by the buyers. This surplus motivates sellers to charge a lower price. This shortage is clearly NOT equilibrium.
For sake of completeness and for purposes of comparison, the equilibrium condition in the market can be identified by clicking the [Balance] button. Doing so reveals an equilibrium price of 50 cents and an equilibrium quantity (without shortage or surplus) of 400 tapes.

Recommended Citation:MARKET DISEQUILIBRIUM, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2024. [Accessed: May 3, 2024].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
GREEN LOGIGUIN
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time at a garage sale hoping to buy either a desktop calendar with all federal and state holidays highlighted or a half-dozen helium filled balloons. Be on the lookout for broken fingernail clippers.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
General Electric is the only stock from the original 1896 Dow Jones Industrial Average remaining in the current index.
|

|
|
"It is the mark of an educated mind to be able to entertain a thought without accepting it." -- Aristotle
|

|
NYMEX
New York Mercantile Exchange
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


